Engineers play a crucial role in creating a sustainable future by revolutionizing circular economies. But what is a circular economy, and why are engineers essential to its achievement?
Have you ever taken a moment to reflect on the amount of waste you generate daily? If you still need to, consider this: the World Bank estimates that the world produces 2.01 billion tonnes of municipal solid waste annually, a volume far exceeding the planet’s capacity to break it down.
However, this issue isn’t solely the fault of industries. The throwaway culture of humans, which emphasizes the production, use, and disposal of goods, also plays a significant role. To address this problem, many have advocated for a transition to a circular economy.
But what exactly is a circular economy, how can it benefit us, and why do engineers feature so prominently in achieving it?
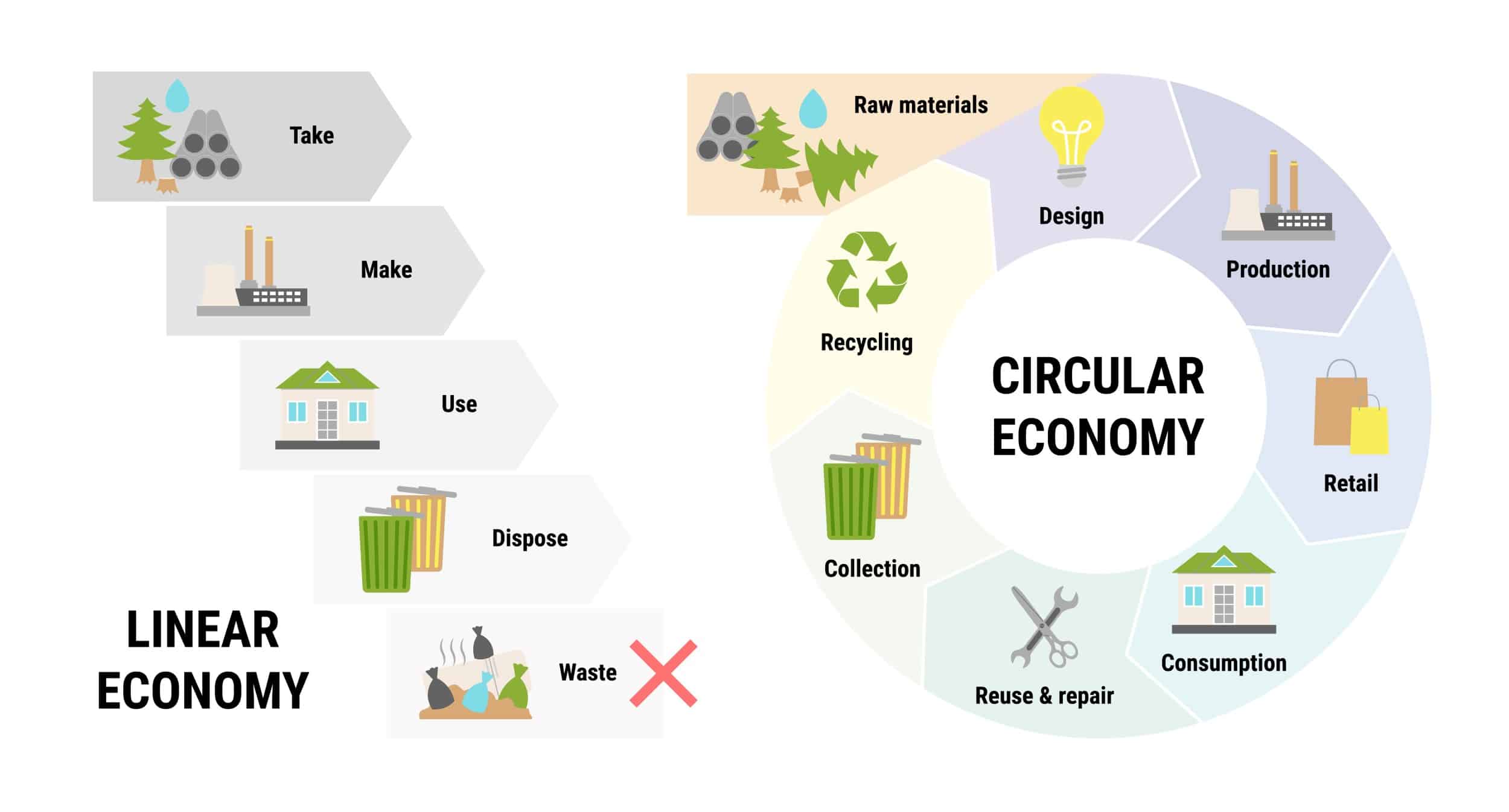
Circular Economy: What’s That?
A circular economy is an economic model that aims to keep resources in use for as long as possible by promoting renewable energy, reducing waste, and minimizing the consumption of non-renewable resources.
At its core, circular economy designs products and systems that minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. This means focusing on reducing the amount of energy and materials used in production, promoting the reuse and recycling of materials, and developing closed-loop systems that enable remanufacturing and reusing products.
It is also about creating a more resilient and sustainable economy by reducing our reliance on finite resources and promoting renewable energy sources. By adopting circular economy principles, businesses and communities can reduce their environmental impact, increase resource efficiency, and create new economic opportunities.
The circular economy is not just about reducing waste or recycling; it’s about rethinking how we produce, consume, and dispose of resources. It requires a fundamental shift in how we design and operate our economic systems, focusing on sustainability, efficiency, and resilience. By adopting circular economy principles, we can create a more sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.
5 Advantages of a Circular Economy
To appreciate the urgency and necessity of achieving a circular economy, we must consider where we are environmentally, what it means if we don’t act now, and how a circular economy will benefit us all.
As its name suggests, a circular economy means that resources and materials within the economy are kept in use for as long as possible, waste is minimized, and the value of products and materials is maintained for as long as possible. And research shows that we can all benefit from this.
Our current global economy is fueling a climate and biodiversity crisis that threatens the well-being of billions of people worldwide. When implemented correctly and inclusively, a circular economy has the potential to protect an endangered environment, foster social equity, and boost sustainable economic progress.
Therefore, it stands to reason that implementing a circular economy could bring about many advantages, such as:
Reduced Waste: By keeping resources in use for longer and minimizing waste, a circular economy could significantly reduce the environmental impact of traditional linear economic models.
Increased Efficiency: A circular economy can create a closed-loop system where products and materials are reused, repaired, or repurposed, reducing the need for new resources and improving the efficiency of resource use.
Job Creation: A shift towards a circular economy could create new job opportunities in industries such as recycling, repair, and repurposing. This could also lead to increased innovation and entrepreneurship.

Economic Growth: A circular economy has the potential to create new markets for reused, repaired, and repurposed products, leading to economic growth and new business opportunities.
Improved Brand Reputation: Adopting circular economy principles can enhance a company’s brand reputation as consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility.
Engineering Field It Applies to Most
Circular economy principles apply to various engineering fields, including materials, industrial, mechanical, and electrical engineering. These principles aim to promote sustainable practices, minimize waste, and keep resources in use for as long as possible.
• Materials engineers develop new renewable, recyclable, and biodegradable materials while designing products that are easy to disassemble and recycle.
• Industrial engineers optimize production processes to minimize waste and promote the reuse of materials.
• Mechanical engineers design products and systems that are energy-efficient and easy to maintain.
• Electrical engineers focus on developing renewable energy systems and energy-efficient technologies.
Incorporating circular economy principles into all engineering fields can help create a more efficient, resilient, and sustainable economy.
Designing a Circular Economy

Design is critical to transitioning from a linear economy to a circular one. It involves product design, materials design, production systems and processes, and business models. The UK-based Ellen MacArthur Foundation (which works to accelerate the transition to a circular economy) advocates designing waste from products and processes, making reuse, repair, regeneration, remanufacturing, and recycling the standard by design.
The Foundation notes that designing a circular economy cuts across all engineering disciplines and requires new industrial models prioritizing reuse, repair, recycling, eco-design, sustainability, and industrial ecology. Industrial ecology seeks to optimize the total materials cycle from virgin material to finished product, component, obsolete product, and ultimate disposal. The goal is to create an ecosystem in which waste is a valuable resource.
Engineers must adopt a systems thinking approach to design for a circular economy. They must consider the entire life cycle of a product, from its production to its end-of-life stage, and identify ways to minimize waste and optimize resource use. This approach requires collaboration between engineering disciplines and other professionals, including designers, policymakers, and business leaders.
Designing for a circular economy also involves developing new materials and production processes that prioritize resource efficiency and sustainability. Engineers can identify ways to use natural, biodegradable materials instead of manufactured materials like metals and plastics, reducing the reliance on non-renewable resources.
Engineers can develop new materials and production processes prioritizing resource efficiency and sustainability, reducing our reliance on non-renewable resources. However, one must also question what challenges engineers might face in designing a circular economy.
Engineering Implications
It has been well-established that engineers have the potential to play a vital role in driving the shift from a linear economy to a circular one. According to Repurposed Materials, Inc. (a US-based company specializing in finding innovative and sustainable uses for industrial byproducts and waste materials), this transition poses challenges and opportunities for engineers.
“Engineers are experts in systems thinking, which puts them in an excellent position to exert influence and provide leadership. They can help to identify opportunities to optimize product life cycles and create feedback loops that enable the reuse of materials,” said Repurposed Materials, Inc. in a recent article.
They highlighted that engineers’ central challenge is creating ongoing circles of use and reuse so that waste does not exist. For example, engineers need to find ways to support the reuse of products without breaking them down into materials or to create recycling streams that become the source of raw materials for the following line of products.
“They can also identify ways to make greater use of natural, biodegradable materials rather than manufactured materials like metals and plastics,” suggested Repurposed Materials, Inc.
Engineers are encouraged to collaborate with other professionals, including designers, policymakers, and business leaders, to drive the transition to a circular economy. Additionally, engineers can drive innovation by developing new technologies and processes that enable greater resource efficiency and sustainable production.
Despite the challenges engineers will face in designing new supply chain models and creating ongoing circles of use and reuse, Repurposed Materials, Inc. is confident that engineers can drive innovation and help build a sustainable future by collaborating with other professionals.
REFERENCES
What is a Circular Economy? Is it as Important as Reports Suggest?
5 Ways Our Lives Would Improve in a Circular Economy
Engineering in the circular economy
Role Engineers Play in a Circular Economy


